A thesis dissertation is an extensive piece of writing that aims to research a particular subject or social phenomenon. The aim of the thesis dissertation is to produce an original and unique piece of academic research that revolves around a well-defined topic or area of research. This substantial piece is usually produced to fulfill the degree requirements of a post-graduate and doctoral program and is quite different from the usual university assignments and reports.
Thesis dissertation writing is a technical and intricate process that requires time, extensive planning and top-notch research skills. So, if you are in the process of writing your thesis dissertation or planning to start your master’s degree program, this article is your go-to guide to understand the basics of writing a well-thought-out thesis dissertation.
What is a thesis?
Students often ask this question from their professors and supervisors: What is a thesis and how is it different from other pieces of writing? A thesis can be defined as a piece of research writing that focuses on a contestable or arguable point or issue that you intend to prove or disprove. You present your justifications by stating facts and figures, along with carrying out your individual research study to examine the evidence that you have collected.
A thesis is usually written to fulfill the requirements of your Master’s or doctoral degree program and is an essential rudiment of your academic or professional qualification. It is an original piece of writing about a particular subject or phenomenon that adds new evidence to the already existing body of knowledge and substantiates the researcher’s hypothesis or research questions.

What is a thesis statement?
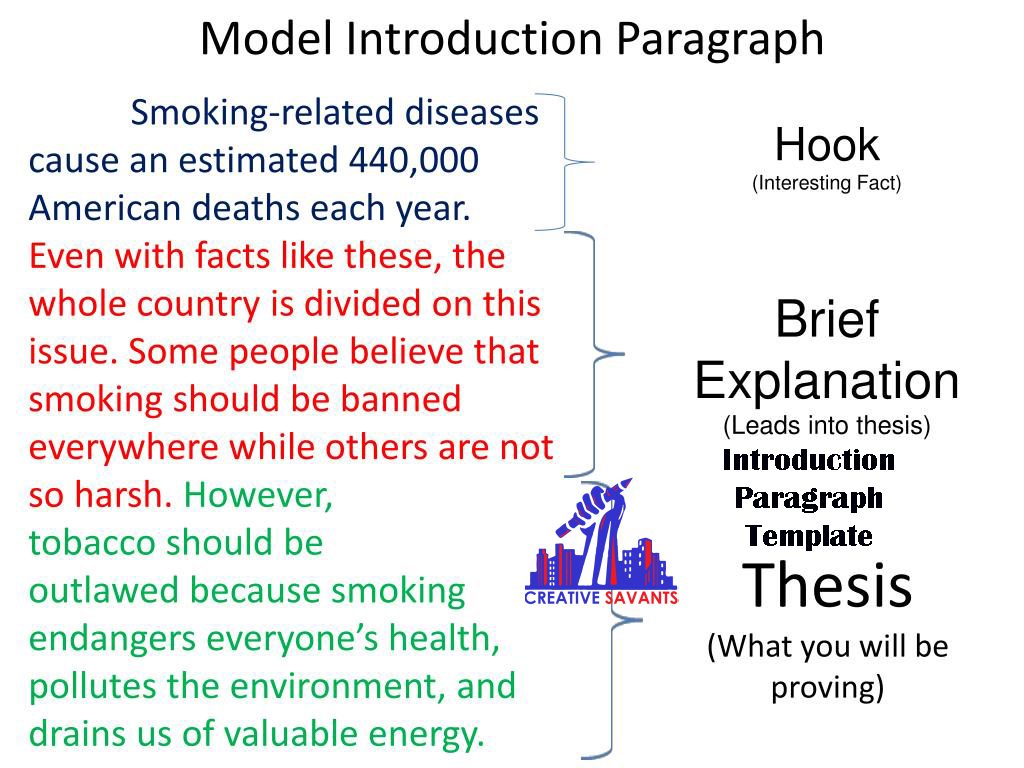
A thesis statement is an integral part of academic essay or research paper, as it gives a direction to the writer and helps him/her to stay focused. This one sentence statement is the crux of your argument and sums up the central point of your paper or essay. The thesis statement establishes the purpose of the writer and declares his/her position or stance on the specific subject. This crucial aspect is usually placed in the introduction section and summarizes the conclusion that the writer has reached during the course of completing the research endeavor.
How to Write a Thesis Statement?
A good thesis statement acts as a roadmap for the writer and explains what message you intend to give to your audience. To organize your thought process and build a strong and credible thesis statement, following are some easy steps that you can follow to write your thesis statement:
- Convert your research topic into a thesis question
- Brainstorm different solutions for the thesis question and explore what information is already available
- Pick the most suitable solution for your thesis question
- Develop a thesis roadmap by brainstorming the best reasons behind picking this particular solution
- Explain how your solution and reasons are different from other researchers and emphasis your research, solutions and reasoning
- Combine all the information and formulate a sentence

Types of thesis statement
Thesis statements can be of various types. Following are some common types of thesis statements:
- Thesis statements that explain a particular phenomenon
- Thesis statements that evaluate a particular phenomenon
- Thesis statements that assert a phenomenon or cause
- Thesis statements that focus on a particular argument
Elements of a Compelling Thesis Statement
- A good thesis statement is concise and explains your perspective in just one or two sentences
- It is not just a thorough explanation of a fact or statement that everyone already knows, but a claim and argument that needs further evidence and analysis to back it up
- It is coherent and focuses on pertinent aspects of the topic, combining all the elements as a whole and in the form of one main idea
Creative Savants can help you write engaging and compelling thesis statements for your Master’s or Doctoral Thesis Dissertation. We offer the best dissertation writing services and can help you secure the grade of your dreams.
Elements in a Thesis Dissertation
Every research begins with a question. What are the causes and effects of this particular social phenomenon? What methods can be employed to resolve this particular issue at hand? How can this study contribute to the existing body of knowledge? Once you have a question, your job as a researcher is to seek credible and relevant information pertaining to the topic under discussion. You look for theories that can help you in better understanding the topic under discussion and how its postulates can help in drawing meaningful scientific solutions.

Apart from writing a compelling thesis statement, there are other elements of a thesis dissertation as well that requires proper execution. After selecting a thesis statement, which acts as the premise of the research, you start working on other elements or steps of the thesis writing process to effectively defend your arguments, explain the data processing procedures and aptly present your findings and conclusions for the readers. Following are some significant elements in a thesis dissertation:
Dissertation Title
The title of the thesis explains to the reader the purpose of conducting the research and the themes and content of the study. This precise statement defines the main topic and outlines the independent and dependent variables. The title allows other researchers to find your research and outline a brief outline of your study, research methodology and key participants.
Components of a dissertation title
A compelling dissertation title encompasses several components, and each component signifies something pertinent about your study to the reader. Following are some important components of a dissertation title:
Defines the focus and area of interest
A compelling dissertation title should indicate the central focus of your research and the key area of interest. The area of interest can be defined as the broader theme of your study, while focus is the particular angle it will be directed towards. The area of interest also sheds light on the theory that underpins your research endeavor. Since you have limited words, to sum up, your title, it is important to mention the area of research and skip the focus component.
Mention the outcome of your research
Whether you are working on an empirical study or a theoretical one or a combination of both, you need to mention the outcomes of your study in the title to draw the attention of the reader. However, these outcomes may highlight just one or two aspects of your study rather than all the major findings. Also, the author must focus on facts that can provide valuable lessons to the reader as well as address specific problems or challenges.
Important components of your research plan
Your title must include other important aspects of your research plan as well, including the research methodology, research design and data analysis techniques. For instance, to mention the research design, you can use qualitative and quantitative in your title. Similarly, to mention the research methodology you can use case study and ethnographic study etc. in the title.
Abstract
An abstract is a brief description of your research study that summarizes your purpose, methodology and findings. A typical abstract is about 350 words or less and includes five fundamental aspects of your study, including thesis statement, objective, methodology, findings and conclusion. An abstract is usually the last thing you write and it illustrates your understanding of the topic and the related sources you have studied for the completion of your dissertation.
Elements of Abstract writing
Define your objectives/purpose
The first element of the abstract is to define your research objectives or the question that you aim to answer through this research study. It can be a social issue or a topic of academic relevance. The key is to state your problem and purpose concisely by using different verbs like investigate, evaluate, describe, examine or test. This part of the abstract should be written in present or past simple tense.
Research methodology
In this section, you indicate your research methodology to the reader and provide a simple description of this approach in one or two lines. It is usually written in the past simple tense and defines completed actions like detailed interviews were conducted/will be conducted for 200 participants. The key is to provide quick insight to the reader about your research procedures and not highlight the strengths and weaknesses of this method.

State results/findings
In this section, you summarize your findings in the present or past simple tense. The idea is to state the most important facts that can support your conclusion. For instance: the study has shown that a strong correlation is present between caffeine and productivity levels.
Conclusion
This is the last section of your abstract which presents the central point of your study and is written in present simple tense. If there are some pertinent limitations to your research, you can also mention them here, as it allows the reader to evaluate the credibility of your research study.
Keywords
At the end of your abstract, you are required to add a list of keywords that can help future researchers and potential readers to find your dissertation, while conducting their own literature review searches. However, be aware of the different referencing styles, as they have their specific formatting guidelines for these keywords
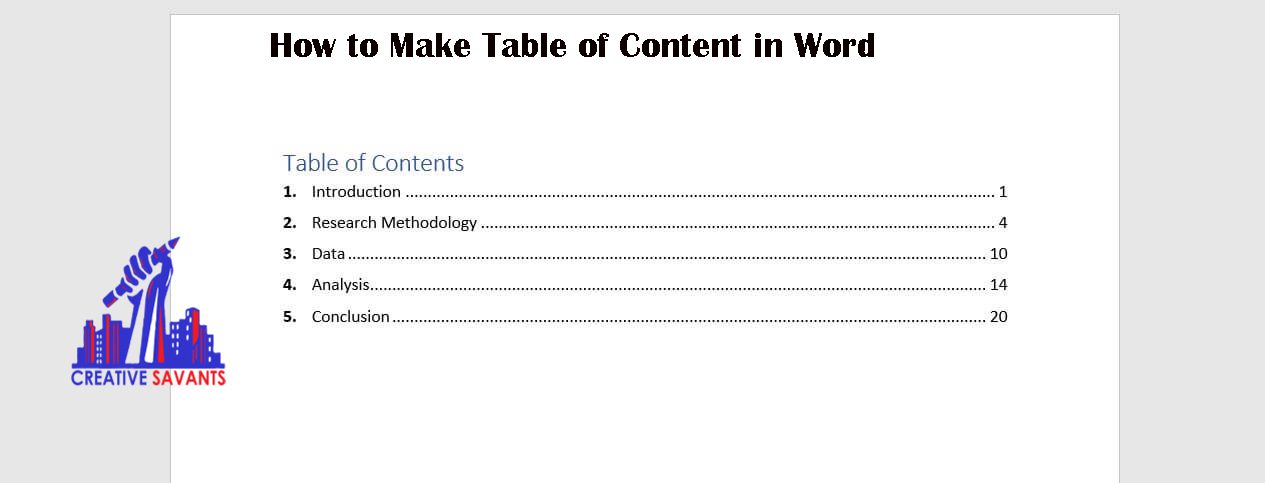
Table of Contents
The table of contents is a numbered and organized list of chapters or major sections of your thesis dissertation. This automated table allows the reader to skip down to the most relevant sections. A clear and well-formatted table of content is an integral part of the research document.
Checklist for TOC:
- Should be well-formatted
- Should list all the sections of the document, starting from the thesis dedication page. If there is no dedication page, this table should start from the abstract page
- You must list all the titles of the page and the main sections of each chapter. You are not required to list subsections. You can choose headings 1, 2, 3 and 4 from the dialogue box placed on the extreme right of the Home tab on a standard Microsoft word document
- All page numbers should be double-checked to avoid errors
How to make a table of contents page?
The table of contents can be generated automatically, as a range of pre-formatted styles are available on the Microsoft word application. After completing headings and titles:
- Click on the reference tab
- TOC tab is placed on the extreme left side of the document
- You can update the TOC table as per changes in your document. Click on the update table option and you can update page numbers or the entire table, if needed
Introduction
This section of the thesis dissertation explains the importance and rationale of the study. It provides a summary of the background information, executive summary, significance of research study, research problem, research questions, and hypothesis. This section also explains the data collection and analysis methods, along with providing definitions and limitations and delimitations of the study. The introduction section establishes the researcher’s niche or subject area, explains the researcher’s views about the topic and presents hypothesis and research questions.
How to Write a Thesis Introduction?
Identify your target audience
The first step of the thesis introduction section is to identify your target audience. Your first priority should be your thesis supervisor, as he will be grading your dissertation. You should also consider the students, academicians and subject specialists of your research area or specialization.
Engage the reader
The first sentence of your paper is extremely crucial, as it will lay down the structure or outline for the preceding sections. Ask yourself: How many papers have you left unread because of their weak first paragraphs. Generally, researchers hook readers by asking a question or using a quotation in the first paragraph. The best way is to start your introduction section with a broad and interesting sentence that can engage the reader and can provide a seamless transition into your main argument.
Relevant background information
A good introduction includes relevant background information, so the reader can develop a better understanding of the topic under discussion, as well as your arguments and thesis statement. Moderate background information should be added in this section, as the idea is to share some pertinent background research endeavors with the reader, along with highlighting their relevance for this study.
Educate the reader about the purpose of the thesis
Brief the reader about the purpose of the study as well as the motivation for your thesis dissertation. Explain the topic, scope of your research, its relevance and what scientific situation the topic is related to in this section.
Give key points and the thesis statement
Mention all the key points in this section, so the reader can develop a thorough understanding of the main argument. End this section with your thesis statement, a one or two-line sentence that summarizes your main supporting ideas.
Literature Review
A literature review is one of the most challenging and complicated sections of thesis writing. In this unit, the researcher analyses available literature that is relevant to his/her research topic. They study literature to build the theoretical framework, access historical events and dig out content that can support their research objectives.
The thesis dissertation is grounded in the literature review section, as it presents a diverse range of arguments by authors, researchers and academicians that can support your main argument. One of the most common mistakes that students make while writing a literature review is that they use direct quotes rather than paraphrasing these findings, which ultimately increases the plagiarism count.
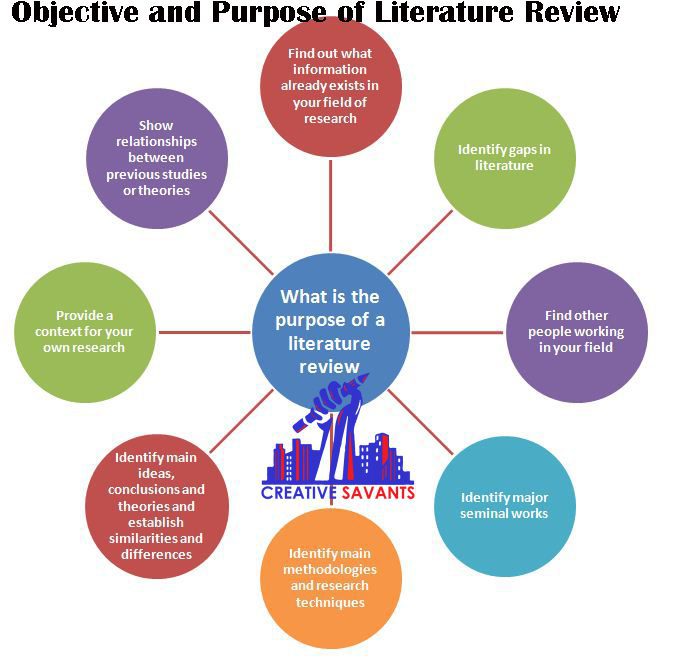
How to Write a Compelling Literature Review?
Search for relevant literature
The first step to writing an engaging or compelling literature review is to clearly define your topic and begin looking for literature. For thesis writing, focus on literature that is relevant to your research problem. Try making a list of keywords, as it will help you to search for credible research studies. You can also consult your university’s library catalog.
Evaluate your sources and select the best ones
You might end up reading and researching an array of research published on your research topic. However, try and make a list of these sources and evaluate which ones are most relevant for your research objectives. Ask questions such as “has the author addressed a significant research question, or described any key terms that can help you in your research.” Try using Google Scholar, as it includes high citation count research papers that are regarded as influential and credible sources of information. Remember to keep a check on your sources for referencing and citations.
Identify themes and patterns
After selecting sources, start organizing your literature and try to understand the themes, patterns and gaps in them. Identify what theories, methods and research designs have been used by researchers. Check what debates, contradictions and conflicts the researchers have engaged in and whether your sources have agreed or disagreed with them. Carefully evaluate the missing gaps in the existing literature. You can base your research on these weaknesses and address areas that need further research or clarity.
Structure it well
Like any other academic writing, a literature review should also have an introduction, the main body and a conclusion section. The text in each section is based on the objectives and aims of your study.
The introduction should focus on the purpose of the literature review and should emphasize upon your research problem, timeliness of the topic or gaps in the existing literature. The main body should include all those researches that support your main argument. For clarity, you can divide these body paragraphs into different subsections. In this section, you should synthesize and summarize information, analyze it and discuss its significance for your study.
In conclusion, you have to summarize all the key points of your findings and focus on their pertinence. You can highlight how your research addresses the weaknesses of previous research endeavors and how it can potentially fill the missing gaps to build theoretical frameworks.
Read more: How to draft literature review for research papers
Research Methodology
In this section, the researcher explains the research design and the analysis procedures that will be used to collect and access research data. The researcher defines the sample, the sampling technique and the method that will be employed to collect data. A clear description is provided by the student, so the reader can follow each and every step involved in conducting the research.
This section provides a comprehensive description of the research process that can easily be replicated by future researchers, by employing similar or different conditions. Bear in mind that the research methodology section is all about testing your research hypothesis, and ensuring that all your research questions are answered well.
How to Write a Research Methodology Section in Thesis Dissertation?
Explain your research method
The first step is to introduce your research method and explain it well to the readers. Elucidate how this research method can help you in answering your research question and is the most suitable approach for this thesis dissertation. Also, highlight the validity and reliability criteria in this type of research design
Explain data collection methods
After explaining the research method, explain your data collection tools to the readers. These can either be qualitative, quantitative or a mixture of both. Explain how you will operationalize variables and how these methods will help future researchers to replicate the findings of your research study.
Explain data analysis method
After specifying the data collection tool, indicate what method would be employed to analyze the data. Avoid going into too much detail at this stage, as you are not presenting the results of your study, but just discussing the method. You can use SPSS software to analyze the data, t-test or linear regression model for statistical testing and content analysis for coding data etc.
Justify your methodological choices
In this section, you need to justify all your choices and state why you chose these specific methods for the research study. You can also discuss why other methods were not appropriate or suitable for hypothesis testing or research questions. Furthermore, you can also acknowledge the limitations of your approaches, however, justify your choice by mentioning the strengths of these approaches.
Data Analysis
In this section, the researcher discusses the findings of the study by employing data analysis tools. In qualitative research design, the researcher can use focus groups, interviews, content analysis methods etc. to identify concepts, patterns and opinions in non-numerical data. In quantitative research design, the researcher can use surveys, correlational studies and causal-comparative studies to access numerical data.
Tips for Writing Data Analysis Section
Relevance
Never follow the collected data blindly. The key is to ensure that the collected data is sufficient to provide answers to your research objectives. All the presented data should be relevant and based upon the objectives and aims of the study. Scrutiny of the data should be on the same lines as that of the literature review section. Explain the reasoning behind your data collection method and analysis technique to the reader so they critically evaluate its relevance to your study.
Analysis methods
Use methods that are appropriate for data collection and research objectives. The reasoning behind this is to explain as well justify this data collection method. Remember, the reader should be aware of the reasoning behind the selection of this analysis method and what research was carried out to make this choice. Inform the reader how this method will allow you to identify patterns and relationships between variables, meaningfully.
Selection of quantitative or qualitative research design
Quantitative research design is employed for scientific and technical research work, as it involves statistical and numerical analysis. On the other hand, qualitative research design helps in identifying themes, patterns and relationships between variables that cannot be represented statistically or numerically. Choose your research design wisely.
Remove biases
One common mistake committed by researchers during the data collection process is the inculcation of their own opinions and biases in the finding. Remember, the data should be meticulous so that it can speak for itself. It should be valid and reliable to support or refute an argument and should critically evaluate a phenomenon, with no biases or errors.
Use graphs, charts and diagrams
To demonstrate large chunks of the data, you can use a range of graphs, charts and diagrams. Tables are an excellent way to present both qualitative and quantitative data, meaningfully. Always, keep your reader in mind, while presenting your data. While a particular diagram or chart may be clear to you, it can be unclear for someone who is not familiar with this research area.
Discussion
This section is all about presenting your findings in relation to the theories that you have applied to build a connection and support your main arguments. In this section, you discuss your findings, state the limitations of your study, propose advice for future researchers and discuss areas that need further exploration. The researcher presents his/her findings by using previous information and summarizes the data to support their research objectives. You can also add recommendations in this section to future researchers to improvise the outcomes of the research study.
How to Write an Engaging Discussion Section?
Summarize your key findings
Start this section by stating your research problem and summarizing your key findings. Remember, the idea is to simplify your findings for the layman and not to copy-paste the data and tables. You have to provide answers to your research question and interpret the data to the readers.
Provide interpretations
The results might be obvious for the reader, however, the idea is to carefully explain the reader and provide interpretations of the answers to your research questions. You will identify the patterns and relationships among variables, discuss results that support your hypothesis, highlight unexplained results, provide alternative explanations and make arguments, and compare your findings to previous research.
Discuss the implications
After providing interpretations, you relate your findings with the surveyed literature review and draw connections. You try to fit your findings in the context of existing knowledge, along with highlighting its implications and consequences for theory or practice. You assess whether your results support previous research findings or challenge the existing theories.

Admit your limitations
Even the best researchers acknowledge their limitations and assess the credibility of their research findings. Limitations are not mere errors in the research process, but an accurate picture of your unanticipated obstacles and the challenges you faced during the entire process. Remember, only mention those limitations that are relevant to your research objectives and assess the impact they had on the results. For instance, a small sample size or issue of generalizability.
Also See: Excellent Ways On Persuasive Writing Bullet Points
Conclusion
In this section, you summarize all the textual information in the thesis dissertation and remind the reader about all the main arguments and answers. You restate your research question or hypothesis, discuss your findings, highlight the contribution of your study to the available pool of literature, mention limitations and provide guidelines to future researchers. Remember, no new information or argument can be introduced in this section.
How to Write a Thesis Conclusion?
Restate your thesis statement
The best way to start this section is to restate your thesis statement by changing its wording. Avoid repetition and change the structure and wording to make it more appealing for the reader. Also, avoid using apologetic phrases such as ‘this thesis dissertation has tried to highlight.’
Review and restate your main arguments
The next step is to review and restate your main arguments by looking back at the text and making a note of the key points. You can reword these points and incorporate them in the conclusion. You can also quote key statistics and quotations to conclude your research and present your closing thoughts. The idea is to fit your introduction into your conclusion section.
Explain the significance and relevance of your study
State the significance and relevance of your study to the reader, encouraging them to question their opinions and reflect on your findings. The idea is to explain why your study is ground-breaking and how it substantially contributes to the existing body of information.
Give a valuable message to the reader
Conclude your thesis dissertation with a recommendation, question or a call to action. You can also guide future researchers or explain how this problem will remain relevant in the coming times. If you begin your thesis with a historical example or a quote, you can restate the same event or statement in different wordings. You want the readers to feel well-informed about the topic and are ready to take the needed actions.
How to Format Thesis Dissertation to APA Guidelines?
Thesis writing demands extensive know-how of different referencing formats and style rules. Your supervisor will provide you with specific guidelines related to the format your university follows. A majority of universities use APA guidelines and rules for referencing and formatting style. The APA citation style or American Psychological Association style is one the most widely used referencing and citation styles. It is commonly used for education, social sciences, psychology and scientific thesis writing projects.
The APA Formatting Rules for Thesis Writing are as follow:
Page Layout
The page layout must be 1 inch from all sides with a standard US letter size of 8.5 x 11. The majority of thesis dissertations require a larger margin size, often specified by the university guidelines. Other than the copyright and title page, all pages of the document must be numbered right, with an appendices chapter at the end of the document.
Text
All the text should have flush-left justification, with text unjustified on the right edge of the document. The first line of each paragraph should be indented by 0.5, except for the abstract paragraphs. Avoid single line text alone, either at the top or bottom of the text. The text should be double spaced, and none of the text should be italicized for emphasis. All the sentences should begin with a capital letter and end with a period. Bullets should either be circles or squares.
Header
The header should be within the document and not below the margin. The title pages should have a running header stating TITLE OF PAPER. The next pages should follow the same running header. Some universities instruct students to use roman numerals instead of running heads.
Preliminary Pages
All the pages should be marked with lower case roman numerals, except the copyright and title page. The university may provide you with their own format for the title and copyright pages, however, you can find examples on the internet as well.
Headings
The heading should be marked as Heading 1, 2, 3, 4 and onwards. Before major heading levels 1 or 2, triple or quadruple spaces should be given. All headings within the document must be arranged in the below-mentioned formatting styles:
Tables
Captions of the tables should be single-spaced, italicized and keywords capitalized. Each table should be numbered which then must be mentioned in the list of tables section in the front section of the thesis dissertation. Never label or refer to tables as the table above or table below. Try to complete one table on one page only. You can place table notes at the end of each table. General pointers related to copyright or attribution should end with a period, while the explanation of abbreviations should be separated with the help of a semicolon.
Figures
The captions of the figure should be italicized and should end with a period. Each figure should be numbered and mentioned in the list of figures in the front section of the thesis dissertation.
Quotations
All quotations must end with a period and should be placed in “”. All quotes of 40 words or more should be formatted as a block and indented by 0.5. If the quote is two paragraphs, the second paragraph should be indented by 1 inch.
References
This intricate section is placed at the end of the document, before appendices and includes a list of all the sources that have been used in the document in alphabetical order. Each entry should use hanging indent format and be double-spaced.
Read more: APA referencing style for thesis dissertation
Appendices
Each appendix should be labeled in a capital letter as Appendix A, Appendix B etc. Each should be placed on a separate list with identifying capital letters, placed on the top of each page. Each appendix can include headings, sub-headings, figures and tables. Each of these must be numbered with the identifying capital letter as Table A1, Table B2 etc.
Significance of Proofreading Thesis Dissertation
Thesis writing is a monumental task that requires years of research and multiple rounds of editing. Proofreading is the second toughest part of thesis writing, as it requires you to read, edit and rewrite different sections of your thesis dissertation. Proofreading is an essential step for ensuring the grammatical and technical accuracy of your thesis dissertation. In this step, you thoroughly check all the sections of your document and edit any typographical or grammatical errors. The key is to access your word choices, check capitalization errors, remove difficult sentences and maintain textual consistency throughout the document.

When it comes to proofreading you have myriad options. The first is to proofread your thesis on your own, however, this requires a lot of time and dedication. Also, proofreading your own work can be a challenge, as the writer’s bias can affect the quality of your work. The second option is to hire one of the best dissertation writing service providers to ensure optimum proofreading services as per the English proofreading standards. These providers have professional and experienced editors that can provide error-free proofreading services.
Do Checkout: The Importance of Proofreading Your Documents
Are you looking for some reliable thesis dissertation providers? Do you need help in proofreading your thesis dissertation without compromising on quality? Creative Savants offer premium thesis writing services, with zero plagiarism and strict adherence to the highest quality standards. Our highly qualified thesis writers and proofreaders are available 24/7 for your timely assistance. So what are you waiting for to contact Creative Savants to draft an exceptionally convincing thesis proposal and win the confidence of your professor, kick-starting your academic journey without any challenge or hindrance?